Research on level of tenofovir in breast milk of HBV-infected mothers by Professor Lin and Jin’s team in International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
2023.02.28Recently, The low level of tenofovir in breast milk supports breastfeeding in HBV-infected mothers has been published in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents by Prof Lin Neng Ming(Department of Pharmacy) and Jin Jie(Department of Infection) from Affiliated Hangzhou First People’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine.
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) is the major route of HBV transmission, and the prevention of MTCT is an important step to achieve the World Health Organization’s goal of eliminating hepatitis B by 2030. Taking Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) by guidelines is recommended as the first-line antiviral therapy during pregnancy due to its high efficacy and high barrier to resistance. However, the safety of breastfed infants whose mothers continue to receive TDF postpartum is uncertain. Recommendations for breastfed infants in current guidelines are predominantly derived from studies of breastfeeding mothers with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), not HBV. Therefore, the safety of breastfeeding during postpartum TDF treatment warrants more research.
Because Tenofovir (TFV) is the active component of TDF, the concentration of TFV was determined in breast milk in this paper. And the infants’ daily TFV dose via breastfeeding was estimated, and it was compared with dose parameters from umbilical cord (UC) blood and amniotic fluid. Infant exposure to TFV from breast milk is much lower than the exposure from placental transfer and swallowing from amniotic fluid. Moreover, the physical growth parameters of infants born to mothers who continued to receive TDF for three months after delivery were collected in a one-year follow-up. The physical growth parameters of all infants in this study were normal. This study contributes to the understanding of the safety of TDF taken during breastfeeding, thereby relieving anxiety in HBV-infected mothers and improving their compliance with breastfeeding recommendations.
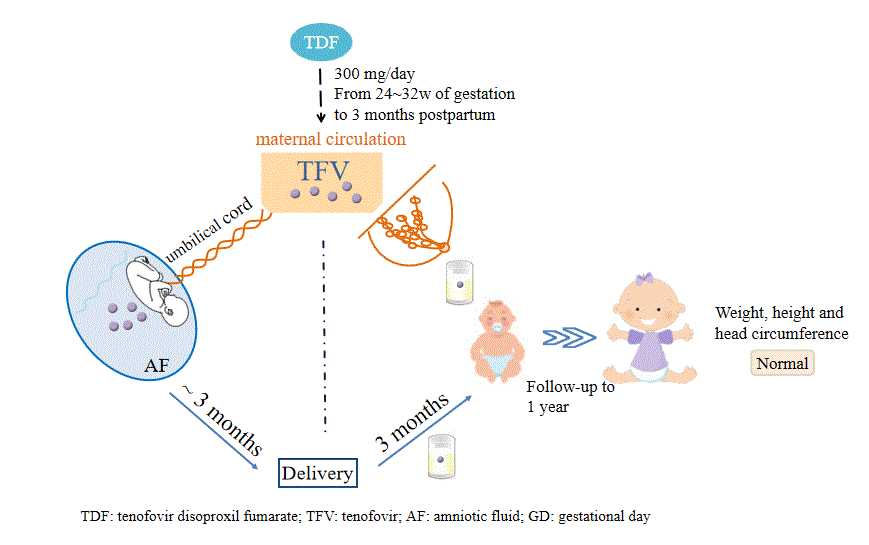
Fig. 1 Graphical abstract
Jin Jie and Li Siying are co-first authors. Lin Nengming and Ma Zhiyuan are co-corresponding authors.


